What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
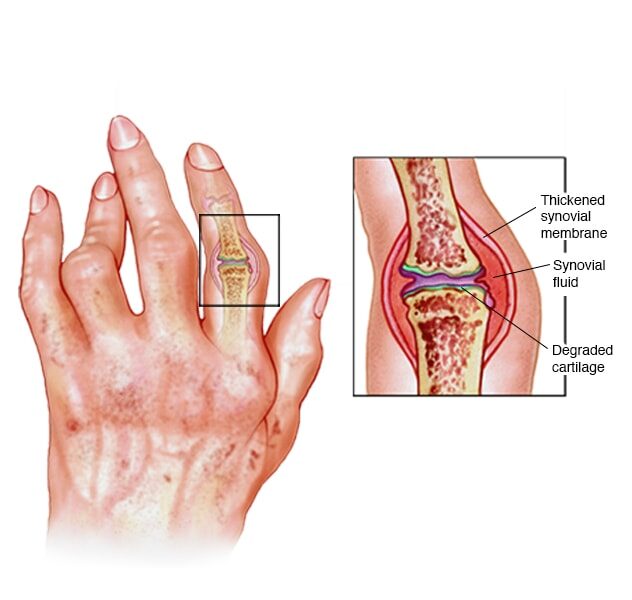
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the joints. It is an autoimmune condition, which means the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. In the case of RA, the immune system targets the synovium, the lining of the joints, causing inflammation. Over time, this inflammation can lead to joint damage, deformities, and disability.
RA can affect people of all ages, but it is most commonly diagnosed between the ages of 30 and 60. Women are more likely to develop RA than men. While the exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is still unknown, researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors may contribute to its development.
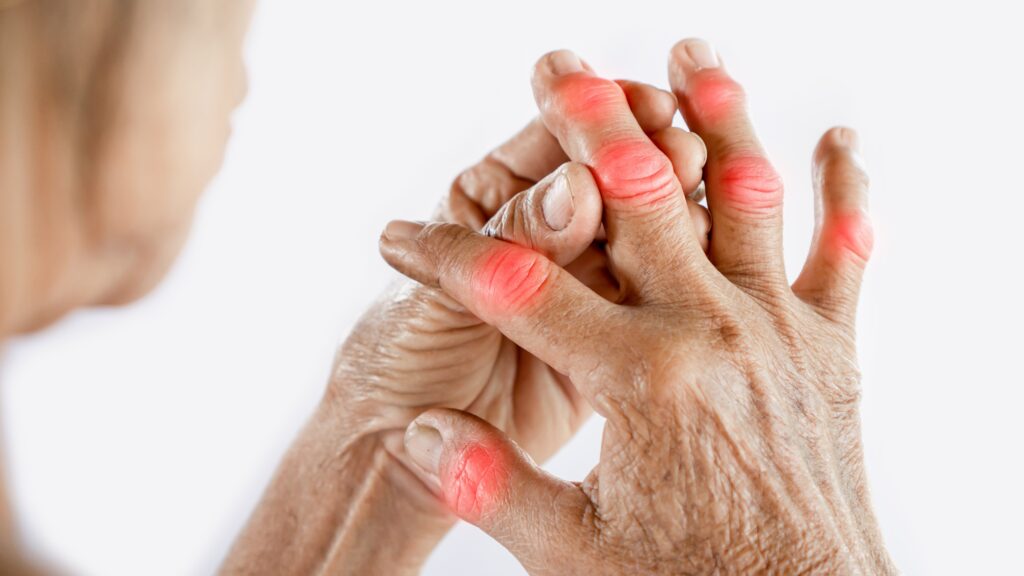
Understanding the basics of rheumatoid arthritis is essential for those living with the condition, as it can help them make informed decisions about their treatment and self-care. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the symptoms, causes, and available treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis, providing you with the knowledge you need to manage your condition effectively.
Symptoms and Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis can present with a wide range of symptoms that can vary from person to person. The most common symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. These symptoms are often symmetrical, meaning they affect the same joints on both sides of the body.
In addition to joint symptoms, individuals with RA may also experience fatigue, loss of appetite, and a general feeling of malaise. Morning stiffness that lasts for more than an hour is another hallmark symptom of rheumatoid arthritis. This stiffness can make it difficult to perform simple tasks in the morning, such as getting out of bed or buttoning a shirt.
As the disease progresses, joint inflammation can lead to joint deformities, such as the classic “swan neck” or “boutonniere” deformities in the fingers. RA can also affect other body systems, including the eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels. It is important to note that the severity and progression of these symptoms can vary greatly from person to person.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and to discuss treatment options.
Causes and Risk Factors of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Although the exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis remains unknown, researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors play a role in its development. Certain genes, specifically the HLA-DRB1 gene, have been found to be associated with an increased risk of developing RA.
Environmental factors, such as smoking and exposure to certain infections, may also contribute to the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Hormonal factors, such as changes during pregnancy or menopause, have also been suggested to play a role in the onset and progression of the disease.
It is important to note that while these factors may increase the risk of developing RA, they do not guarantee the development of the disease. Many individuals with genetic and environmental risk factors never develop rheumatoid arthritis, while others without these risk factors may still be diagnosed with the condition.
Understanding the potential causes and risk factors can help individuals with RA gain a better understanding of their condition and take proactive steps towards managing it effectively.
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging, as there is no single test that definitively confirms the presence of the disease. Instead, healthcare professionals rely on a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests to make a diagnosis.
During the initial evaluation, your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and family history of autoimmune diseases. They will also perform a physical examination to assess the affected joints for swelling, tenderness, and range of motion.
Laboratory tests, such as blood tests, can help support the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. These tests may include:
- Rheumatoid factor (RF) test: This test measures the presence of antibodies commonly found in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. However, it is important to note that not all individuals with RA have a positive RF test, and some individuals without RA may have a positive result.
- Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) test: This test detects the presence of antibodies specific to rheumatoid arthritis. It is highly specific for RA and can help confirm the diagnosis.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) tests: These tests measure markers of inflammation in the body. Elevated levels of ESR and CRP can indicate the presence of inflammation, which is common in RA.
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may also be performed to assess joint damage and monitor disease progression.
A timely and accurate diagnosis is key to effectively managing rheumatoid arthritis and minimizing its impact on your daily life. If you suspect you may have RA, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.
Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
While there is currently no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, there are various treatment options available to help manage the symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. The goals of treatment are to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, preserve joint function, and improve overall quality of life.
The treatment approach for rheumatoid arthritis is typically multi-faceted and may include a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, self-care strategies, and alternative therapies. The specific treatment plan will depend on the individual’s symptoms, disease severity, and other factors.
It is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your unique needs and goals. Regular monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan may be necessary to ensure optimal management of your rheumatoid arthritis.
Let’s explore some of the commonly used treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis in the following sections.
Medications for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Medications are often a cornerstone of rheumatoid arthritis treatment. There are several types of medications that can help reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and slow down joint damage. The specific medications prescribed will depend on the severity of your symptoms and the progression of the disease.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications help reduce pain and inflammation. They are commonly used for mild to moderate symptoms and are available over-the-counter or by prescription.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): DMARDs are a group of medications that can slow down the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and reduce joint damage. They work by targeting the underlying immune system dysfunction that drives the inflammation. Methotrexate is one of the most commonly prescribed DMARDs for RA.
- Biologic response modifiers: Biologics are a newer class of medications that target specific molecules involved in the immune response. They are typically used when DMARDs are not effective or tolerated. Biologics can help reduce inflammation and slow down joint damage. Examples include etanercept and adalimumab.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can provide rapid relief from inflammation and pain. They are often used for short-term management of flare-ups or when other medications are not effective. Long-term use of corticosteroids is generally avoided due to the potential for side effects.
- Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors: JAK inhibitors are a newer class of medications that block specific enzymes involved in the immune response. They can help reduce inflammation and improve symptoms in individuals with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis.
It is important to note that all medications have potential side effects, and the benefits and risks should be carefully considered in consultation with your healthcare provider. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential to ensure the medications are effective and well-tolerated.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care Tips for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
In addition to medications, certain lifestyle changes and self-care strategies can play a significant role in managing rheumatoid arthritis and improving quality of life. Here are some tips to help you effectively manage your condition:
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve joint flexibility, reduce pain, and increase overall strength. Low-impact exercises, such as swimming, cycling, and walking, are generally well-tolerated by individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Balanced diet: Eating a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support overall health and minimize inflammation. Some studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids found in fish may have anti-inflammatory properties and may be beneficial for individuals with RA.
- Stress management: Stress can worsen rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies, or seeking support from friends and family, can help improve your overall well-being.
- Adequate rest and sleep: Fatigue is a common symptom of rheumatoid arthritis. Ensuring you get enough rest and quality sleep can help manage fatigue and promote healing.
- Joint protection: Using assistive devices, such as braces or splints, can help support and protect joints during activities. Additionally, modifying daily tasks or using ergonomic tools can help reduce strain on the joints.
- Heat and cold therapy: Applying heat or cold to affected joints can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Hot packs, warm baths, or cold compresses can be used as part of a comprehensive pain management plan.
Remember, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your lifestyle or starting new exercise routines.
Alternative Therapies for Rheumatoid Arthritis
In addition to conventional treatment approaches, some individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may explore alternative therapies to help manage their symptoms. While the evidence for the effectiveness of these therapies is mixed, some individuals may find them helpful in conjunction with traditional treatments. It is important to discuss any alternative therapies with your healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and appropriate for you. Here are some alternative therapies commonly used for rheumatoid arthritis:
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. Some individuals find acupuncture helpful in reducing pain and improving overall well-being.
- Massage therapy: Massage therapy can help alleviate muscle tension, reduce pain, and improve joint flexibility. It is important to work with a trained massage therapist who is familiar with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Herbal supplements: Certain herbal supplements, such as turmeric, ginger, and Boswellia, have been studied for their potential anti-inflammatory properties. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any herbal supplements, as they may interact with other medications.
- Mind-body techniques: Practices such as yoga, meditation, and tai chi can help reduce stress, improve flexibility, and promote overall well-being. These techniques can be beneficial for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
Alternative therapies should be used as complementary approaches to conventional treatments, rather than as replacements. It is important to have open and honest communication with your healthcare provider about any alternative therapies you are considering.
Coping with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Emotional and Mental Health Support
Living with a chronic condition like rheumatoid arthritis can take a toll on your emotional and mental well-being. In addition to managing physical symptoms, it is essential to prioritize your emotional health and seek support when needed. Here are some strategies to help cope with the emotional impact of rheumatoid arthritis:
- Build a support network: Surround yourself with friends, family, and support groups who understand and empathize with your journey. Sharing experiences and emotions with others who can relate can provide comfort and validation.
- Seek professional help: If you find yourself struggling with anxiety, depression, or other mental health challenges, consider reaching out to a mental health professional. They can provide guidance, support, and strategies to help you navigate the emotional complexities of living with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Practice self-care: Engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation. This can include hobbies, spending time in nature, reading, listening to music, or engaging in creative pursuits. Taking time for self-care can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Educate yourself: Knowledge is power. Educate yourself about rheumatoid arthritis, its treatment options, and self-care strategies. Understanding your condition can help you feel more in control and empowered to make informed decisions about your health.
Remember, it is normal to experience a range of emotions when living with rheumatoid arthritis. Give yourself permission to acknowledge and process these emotions, and seek support when needed.
Conclusion
Living with rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging, but with the right knowledge, support, and treatment, it is possible to effectively manage the condition and improve quality of life. In this article, we have explored the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis. We have discussed the importance of a timely diagnosis, the role of medications in managing symptoms, lifestyle changes and self-care strategies, alternative therapies, and the significance of emotional and mental health support.
Remember, each individual’s journey with rheumatoid arthritis is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and goals.
At our brand, we are committed to providing comprehensive information and support to individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis. Together, let’s tackle rheumatoid arthritis head-on, bringing comfort and relief to those who need it most.