Who Is a Financial planner
A financial planner is a professional who helps individuals and families manage their finances, plan for the future, and achieve their financial goals. They analyze their clients’ financial situations, including income, expenses, assets, and liabilities, to create personalized strategies that maximize their financial well-being. A financial planner takes into account various factors such as age, risk tolerance, and future aspirations to develop a comprehensive plan that addresses short-term and long-term financial needs.

Financial planners offer a wide range of services, including budgeting, investment advice, retirement planning, estate planning, tax planning, and risk management. They can help clients make informed decisions about saving, investing, and spending their money wisely. By providing expert guidance, a financial planner can help individuals and families navigate complex financial landscapes and make educated choices that align with their goals and values.
One of the key roles of a financial planner is to educate their clients about financial matters. They explain complex concepts in a simplified manner, ensuring that clients understand the implications of their financial decisions. This empowers individuals to take control of their finances and make informed choices that contribute to their financial well-being. Overall, a financial planner serves as a trusted advisor, offering personalized strategies and ongoing support to help clients achieve financial success.
The importance of financial planning
Financial planning is a crucial aspect of personal and family finances. It involves setting financial goals, developing a roadmap to achieve them, and regularly reviewing and adjusting the plan as circumstances change. While it may seem overwhelming or time-consuming, financial planning is essential for several reasons.
First and foremost, financial planning provides a clear picture of an individual’s current financial situation. By analyzing income, expenses, assets, and liabilities, a financial planner can identify areas of improvement and develop strategies to optimize financial resources. This understanding enables individuals to make informed decisions about their money and take control of their financial future.
Financial planning also helps individuals and families set realistic financial goals. Whether it’s saving for retirement, buying a home, funding education, or starting a business, having clearly defined goals provides motivation and direction. A financial planner can help break down these goals into smaller, manageable steps and create a plan to achieve them. This not only increases the likelihood of success but also ensures that resources are allocated efficiently.
Furthermore, financial planning helps individuals prepare for unexpected events and mitigate risks. By analyzing potential risks such as job loss, medical emergencies, or market downturns, a financial planner can recommend strategies to protect assets and minimize the impact of these events. This includes establishing emergency funds, obtaining insurance coverage, and diversifying investments. Through proactive risk management, individuals can safeguard their financial well-being and gain peace of mind.
In summary, financial planning is crucial for individuals and families to achieve their financial goals, make informed decisions, and navigate unexpected events. It provides a roadmap for success, empowers individuals to take control of their finances, and ensures that resources are allocated efficiently. By working with a financial planner, individuals can benefit from expert guidance and personalized strategies tailored to their unique circumstances.
Qualifications and certifications for financial planners
When seeking the services of a financial planner, it’s important to ensure that they possess the necessary qualifications and certifications. These credentials demonstrate their knowledge, expertise, and commitment to ethical standards. Here are some of the key qualifications and certifications to look for when choosing a financial planner:
- Certified Financial Planner (CFP): The CFP certification is considered one of the most widely recognized and respected certifications in the financial planning industry. To become a CFP, individuals must meet specific education requirements, pass a comprehensive examination, have relevant work experience, and adhere to a strict code of ethics. CFP professionals have a broad understanding of financial planning principles and can provide comprehensive advice across various areas of personal finance.
- Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA): The CFA designation is a globally recognized credential for investment professionals. While CFAs primarily focus on investment analysis and portfolio management, their expertise is valuable when working with a financial planner. CFAs undergo a rigorous program of study and must pass three levels of examinations. They possess in-depth knowledge of investment principles, financial markets, and asset valuation.
- Chartered Financial Consultant (ChFC): The ChFC designation is awarded to professionals who specialize in comprehensive financial planning. ChFCs undergo extensive training in areas such as insurance, investments, taxes, retirement planning, and estate planning. They are equipped to provide holistic advice and develop comprehensive financial plans tailored to individual needs.
- Personal Financial Specialist (PFS): The PFS credential is offered by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). It is awarded to CPAs who demonstrate expertise in personal financial planning. PFS professionals have a deep understanding of tax planning, retirement planning, estate planning, and risk management. Their knowledge of tax laws and regulations can be particularly valuable when developing financial plans.
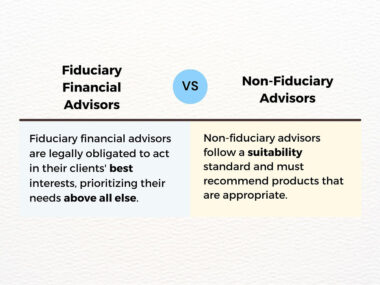
- Registered Investment Advisor (RIA): RIAs are financial professionals who are registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or state securities regulators. They are legally bound to act in their clients’ best interests and must adhere to fiduciary standards. Working with an RIA ensures that the financial planner is committed to providing unbiased advice and putting clients’ interests first.
It’s important to note that credentials alone do not guarantee the quality of a financial planner’s services. When selecting a financial planner, it’s advisable to consider their experience, track record, and reputation in addition to their qualifications and certifications. Conducting thorough research, seeking recommendations, and conducting interviews can help ensure that the chosen financial planner is well-suited to meet individual financial needs.
Steps to becoming a financial planner
Becoming a financial planner requires a combination of education, experience, and professional development. The following steps outline the path to becoming a financial planner:
- Obtain a bachelor’s degree: While a specific major is not required, pursuing a degree in finance, economics, accounting, or a related field can provide a strong foundation in financial principles. Coursework in investments, taxation, and financial planning can be particularly beneficial.
- Gain relevant work experience: Many financial planners start their careers in entry-level positions within financial services firms or advisory firms. This allows them to gain practical experience and develop a deep understanding of financial products, markets, and client needs. Some individuals choose to work as paraplanners or financial planning assistants before transitioning into a financial planner role.
- Pursue advanced education: While not mandatory, obtaining a master’s degree in financial planning or a related field can enhance a financial planner’s knowledge and career prospects. Advanced degrees provide a deeper understanding of financial planning principles, research methodologies, and advanced financial topics.
- Complete a recognized financial planning program: Many universities, colleges, and professional organizations offer financial planning programs that cover the core areas of financial planning. These programs provide a comprehensive understanding of financial planning principles, investment analysis, risk management, tax planning, and retirement planning. Some programs are aligned with specific certifications, such as the CFP certification.
- Gain professional certifications: Obtaining professional certifications, such as the CFP, CFA, or ChFC, can greatly enhance a financial planner’s credentials and expertise. These certifications typically require passing rigorous examinations, demonstrating relevant work experience, and adhering to ethical standards. They showcase a financial planner’s commitment to professional development and adherence to industry best practices.
- Continuing education and professional development: Financial planning is a constantly evolving field, with new regulations, products, and strategies emerging regularly. It’s essential for financial planners to stay up-to-date with industry trends and best practices through continuing education and professional development. This can include attending conferences, workshops, and webinars, as well as participating in industry associations and networks.
Becoming a financial planner is a journey that requires dedication, ongoing learning, and a commitment to ethical standards. By following these steps, individuals can develop the knowledge, skills, and credentials necessary to succeed in the financial planning industry.
Key skills and qualities of a successful financial planner
Successful financial planners possess a unique set of skills and qualities that enable them to excel in their profession. Beyond technical knowledge and qualifications, the following skills and qualities are essential for a financial planner’s success:

- Strong communication skills: Financial planners must effectively communicate complex financial concepts to clients in a clear and understandable manner. This includes active listening, asking probing questions, and explaining options and recommendations in plain language. Clear communication builds trust and ensures clients are well-informed to make informed financial decisions.
- Empathy and interpersonal skills: Financial planning is a highly personal and intimate process. Successful financial planners are empathetic, compassionate, and able to build strong relationships with their clients. They understand their clients’ unique needs, goals, and concerns and tailor their advice accordingly. Building trust and rapport is crucial for long-term client relationships.
- Analytical and problem-solving skills: Financial planners analyze complex financial data, identify patterns, and develop solutions to meet clients’ goals. Strong analytical and problem-solving skills enable financial planners to evaluate various options, assess risks, and recommend strategies that align with clients’ financial objectives. Attention to detail and critical thinking are essential in this process.
- Ethical and professional conduct: Financial planners have a fiduciary duty to act in their clients’ best interests. They must adhere to ethical standards, maintain confidentiality, and avoid conflicts of interest. Trust and integrity are the foundation of a successful financial planning practice. Financial planners must prioritize their clients’ needs and act with honesty and transparency.
- Flexibility and adaptability: The financial landscape is constantly evolving, with new regulations, products, and market conditions emerging. Successful financial planners are adaptable and able to navigate changing circumstances. They can adjust their strategies, recommendations, and plans to accommodate clients’ evolving needs and goals.
- Continuous learning and professional development: Financial planning is a dynamic field, and successful financial planners are committed to ongoing learning and professional development. They stay abreast of industry trends, changes in regulations, and new financial products and strategies. Continuous learning ensures that financial planners provide the most up-to-date advice and solutions to their clients.
By combining technical expertise with these skills and qualities, financial planners can provide comprehensive, personalized advice and guidance to their clients. These attributes contribute to building long-term client relationships, fostering trust, and achieving financial success.
Different types of financial planning services
Financial planning services encompass a wide range of areas and can be tailored to suit individual needs and goals. Here are some of the different types of financial planning services that individuals may consider:
- Retirement planning: Retirement planning involves creating a strategy to accumulate sufficient funds and income streams to support a comfortable retirement. A financial planner can help individuals calculate their retirement needs, determine appropriate savings rates, evaluate investment options, and develop a withdrawal strategy during retirement.
- Investment planning: Investment planning focuses on maximizing investment returns while managing risk. A financial planner can help individuals identify suitable investment opportunities, construct diversified portfolios, and regularly monitor and rebalance investments. They consider factors such as risk tolerance, time horizon, and investment objectives when developing investment plans.
- Tax planning: Tax planning involves strategies to minimize tax liabilities and optimize financial decisions. A financial planner can help individuals make tax-efficient investment choices, take advantage of tax deductions and credits, and plan for major financial events that may have tax implications. Tax planning can help individuals maximize their after-tax income and preserve wealth.
- Estate planning: Estate planning involves preparing for the transfer of assets upon death and ensuring that individuals’ wishes are carried out. A financial planner can work with individuals to develop estate plans, including wills, trusts, beneficiary designations, and powers of attorney. They consider factors such as estate taxes, asset protection, and charitable giving when creating comprehensive estate plans.
- Risk management: Risk management involves strategies to protect against unforeseen events and mitigate potential financial losses. A financial planner can help individuals assess their insurance needs, including life insurance, disability insurance, long-term care insurance, and property and casualty insurance. They ensure that individuals are adequately protected and prepared for unexpected circumstances.
- Education planning: Education planning involves saving for higher education expenses, such as college or university tuition. A financial planner can help individuals estimate the future costs of education, explore different savings options, and develop a plan to achieve education funding goals. They consider factors such as time horizon, risk tolerance, and available education savings vehicles.
- Debt management: Debt management focuses on strategies to effectively manage and reduce debt. A financial planner can help individuals create a plan to pay off debt efficiently, negotiate with creditors, and develop strategies to avoid future debt. Debt management can help individuals regain control of their finances and improve their overall financial well-being.
These are just a few examples of the different types of financial planning services available. Depending on individual needs and goals, a financial planner can offer customized solutions that address specific financial concerns and objectives. By working with a financial planner, individuals can benefit from expert advice and strategies tailored to their unique circumstances.
Creating a comprehensive financial plan
Creating a comprehensive financial plan is a crucial step in achieving financial goals and securing long-term financial well-being. A financial plan serves as a roadmap that outlines individual objectives, strategies to achieve them, and a timeline for implementation. Here are the key components of a comprehensive financial plan:
- Goal setting: The first step in creating a financial plan is to define specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. These goals can be short-term (e.g., saving for a vacation), medium-term (e.g., buying a home), or long-term (e.g., retirement). Setting clear goals provides direction and motivation for the financial planning process.
- Financial assessment: A financial planner conducts a thorough assessment of an individual’s financial situation, including income, expenses, assets, and liabilities. This assessment provides a clear understanding of the current financial position and helps identify areas for improvement or