First Aid
In today’s fast-paced world, accidents can happen anytime, anywhere. That’s why having basic first aid knowledge is crucial for everyone. Whether you’re at home, work, or out and about, being equipped with the skills to provide immediate help can make all the difference in an emergency situation. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of first aid and cover everything from treating burns and cuts to performing CPR and handling fractures.
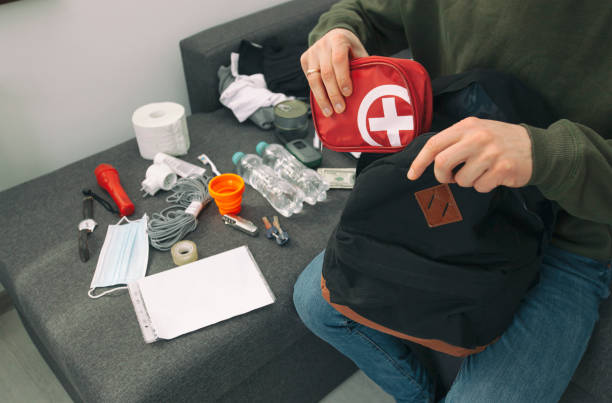

Our brand believes in empowering individuals with essential life-saving information, and this article is no exception. We aim to provide you with clear and concise instructions, so you can confidently step forward when someone needs your help.
Designed to be practical and informative, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to assess and handle a wide range of medical emergencies. By the end, you’ll feel prepared to take action and potentially save lives. So, let’s dive in and arm ourselves with the essential first aid skills that could make all the difference in a critical situation.
Importance of First Aid
First aid is the initial assistance given to a person who is injured or suddenly falls ill before professional medical help arrives. It plays a crucial role in saving lives, preventing further injuries, and promoting recovery. By administering immediate care and stabilizing the patient, first aid can significantly increase their chances of survival and reduce the impact of their injuries.
Having basic first aid knowledge is essential for everyone, regardless of their profession or lifestyle. Accidents can happen anytime and anywhere, from minor incidents like cuts and burns to more severe emergencies such as cardiac arrest or severe allergic reactions. Being prepared to respond appropriately can make a significant difference in the outcome of such situations.
Learning first aid not only equips you with life-saving skills but also boosts your confidence and enables you to take control of emergency situations. It empowers you to provide immediate help and support to those in need, minimizing the potential harm until professional medical assistance is available.
In the next section, we’ll delve into some basic first aid techniques that everyone should know.
Basic First Aid Techniques
Knowing a few basic first aid techniques can make a world of difference when faced with an emergency. These techniques are easy to learn and can be applied in a variety of situations. Here are three fundamental techniques that everyone should be familiar with:
- CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation): CPR is a life-saving technique used in cases of cardiac arrest. It involves chest compressions and rescue breaths to maintain blood circulation and oxygenation. To perform CPR, follow these steps: a. Check for responsiveness. b. Call for help. c. Begin chest compressions. d. Administer rescue breaths. e. Continue CPR until professional help arrives.
- Heimlich Maneuver: The Heimlich maneuver is used to dislodge an object from a person’s airway when they are choking. To perform the Heimlich maneuver, follow these steps: a. Stand behind the person and place your arms around their waist. b. Make a fist with one hand and place it slightly above their navel. c. Grasp your fist with your other hand and give quick upward thrusts. d. Repeat until the object is expelled or the person can breathe again.
- Stop the Bleed: Knowing how to control bleeding is essential in situations where someone is experiencing severe bleeding. To stop the bleed, follow these steps: a. Apply direct pressure to the wound using a clean cloth or your hand. b. Elevate the injured limb if possible. c. Use a tourniquet if bleeding continues and professional help is not immediately available.
By familiarizing yourself with these basic first aid techniques, you’ll have the confidence and skills to respond effectively in critical situations.
Now that we’ve covered the importance of first aid and some basic techniques, let’s move on to exploring common first aid situations.
Common First Aid Situations
Accidents and emergencies can happen at any time, often when we least expect them. It’s crucial to be prepared for common first aid situations, as they can occur in various settings, such as at home, at work, or while participating in outdoor activities. Here are some common first aid situations and how to handle them:
- Burns and Scalds: Burns and scalds can occur from contact with heat, hot liquids, chemicals, or electricity. To provide first aid for burns and scalds, follow these steps: a. Remove the source of heat or stop the burning process. b. Cool the affected area with cold running water for at least 10 minutes. c. Cover the burn with a sterile dressing or clean cloth. d. Seek medical attention for severe burns or if the burn covers a large area.
- Cuts and Wounds: Cuts and wounds can happen due to accidents, falls, or sharp objects. To provide first aid for cuts and wounds, follow these steps: a. Apply gentle pressure to stop bleeding. b. Clean the wound with mild soap and water. c. Cover the wound with a sterile dressing or clean cloth. d. Apply an adhesive bandage or bandage the wound if necessary. e. Monitor for signs of infection and seek medical attention if needed.
- Choking and CPR: Choking occurs when an object becomes lodged in a person’s airway, blocking their ability to breathe. To provide first aid for choking, follow these steps: a. Determine if the person can speak or cough. b. If the person is conscious but unable to breathe, perform the Heimlich maneuver. c. If the person becomes unconscious, perform CPR until professional help arrives.
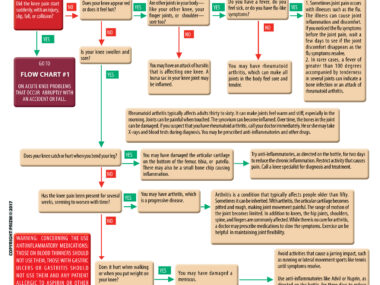
- Fractures and Sprains: Fractures and sprains can occur from falls, accidents, or sports-related activities. To provide first aid for fractures and sprains, follow these steps: a. Immobilize the injured area using a splint or improvised materials. b. Apply ice or a cold pack to reduce swelling. c. Elevate the injured limb if possible. d. Seek medical attention for severe fractures or if the person is unable to move the injured area.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe and can be triggered by food, insect bites, medication, or environmental factors. To provide first aid for allergic reactions, follow these steps: a. Remove the trigger if possible. b. Administer antihistamines if available. c. Monitor the person’s breathing and vitals. d. If the person experiences difficulty breathing or shows signs of anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction), administer epinephrine if available and seek immediate medical attention.
By being knowledgeable and prepared for these common first aid situations, you’ll be able to provide immediate assistance and potentially save lives.
In the next section, we’ll discuss the essential items you should have in your first aid kit.
First Aid Kit Essentials
Having a fully stocked first aid kit is essential for any home, workplace, or outdoor setting. It ensures that you have the necessary supplies to respond to emergencies quickly. While the contents of a first aid kit may vary depending on individual needs and preferences, here are some essential items that should be included:
- Bandages and Dressings: Various sizes of adhesive bandages, sterile gauze pads, and adhesive tape for covering wounds and controlling bleeding.
- Antiseptic Solutions: Antiseptic wipes or solutions, such as hydrogen peroxide or alcohol swabs, for cleaning wounds and preventing infection.
- Adhesive Tape and Scissors: Medical tape and scissors for securing dressings and cutting tape or gauze.
- Disposable Gloves: Latex or nitrile gloves to protect yourself and others from blood-borne pathogens and to maintain proper hygiene.
- Tweezers and Splinter Remover: Tweezers for removing splinters or foreign objects from the skin.
- Pain Relievers and Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, and any prescribed medications specific to your needs.
- Emergency Contact Information: A list of emergency contacts, including local emergency services, your doctor, and any relevant personal contacts.
- CPR Mask or Face Shield: A CPR mask or face shield for performing CPR safely.
- Emergency Blanket: A compact emergency blanket to provide warmth and comfort in case of exposure to cold or shock.
- First Aid Manual: A comprehensive first aid manual or guidebook that provides instructions for various emergency situations.
Remember to regularly check and replenish your first aid kit, ensuring that all items are in good condition and within their expiration dates. Additionally, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the contents of your kit and how to use them effectively.
Now that we’ve covered the essentials of first aid and the items you should have in your first aid kit, let’s move on to specific first aid techniques for different situations.
First Aid for Burns and Scalds
Burns and scalds can occur from various sources, including heat, chemicals, electricity, or steam. It’s essential to act promptly to minimize further damage and provide relief to the affected person. Here’s how to administer first aid for burns and scalds:
- Remove the source of heat or stop the burning process. If the burn is caused by heat, remove the person from the source of heat, or cool the affected area by running it under cold water for at least 10 minutes. For chemical burns, remove any contaminated clothing and rinse the affected area with copious amounts of water.
- Assess the severity of the burn. Burns are classified into three categories: first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree. First-degree burns are superficial and affect only the outer layer of the skin, causing redness and mild pain. Second-degree burns involve the outer layer and the underlying layer of the skin, resulting in redness, swelling, and blistering. Third-degree burns are the most severe and extend through all layers of the skin, sometimes appearing white or charred.
- Provide pain relief and prevent infection. For first-degree burns, you can apply a cool compress or use over-the-counter pain relievers to alleviate pain. For second-degree burns, avoid popping blisters and cover the area with a sterile dressing to prevent infection. For third-degree burns, seek immediate medical attention and avoid applying anything to the burn.
- Seek medical attention for severe burns or large areas of burns. For burns that cover a large area of the body, involve the face, hands, feet, genitals, or major joints, or are caused by chemicals or electricity, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Remember, first aid for burns and scalds is aimed at providing immediate relief and preventing further damage, but professional medical help should be sought for severe burns or those that cover a large area of the body.
Now that we’ve covered first aid for burns and scalds, let’s move on to first aid for cuts and wounds.
First Aid for Cuts and Wounds
Cuts and wounds can occur due to accidents, falls, or sharp objects. Providing prompt first aid for cuts and wounds is crucial to prevent infection and promote healing. Here’s how you can administer first aid for cuts and wounds:
- Apply gentle pressure to stop bleeding. Use a clean cloth or your hand to apply gentle pressure to the wound. If the bleeding is severe and does not stop after a few minutes, apply additional pressure and elevate the injured area.
- Clean the wound. Rinse the wound gently with mild soap and water to remove any dirt or debris. Avoid using hydrogen peroxide or alcohol, as they can damage healthy tissues.
- Cover the wound with a sterile dressing. Apply an antibiotic ointment or sterile dressing to the wound to keep it clean and prevent infection. If the wound is deep or gaping, consult a healthcare professional to determine if stitches are required.
- Apply an adhesive bandage or bandage the wound if necessary. For smaller cuts or wounds, you can apply an adhesive bandage or sterile strip to keep the wound closed and protected. For larger wounds, use sterile gauze pads and adhesive tape to bandage the wound securely.
- Monitor for signs of infection. Keep an eye on the wound for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, pain, warmth, or pus. If you notice any signs of infection, seek medical attention.
Remember, providing first aid for cuts and wounds helps prevent infection and promotes healing. However, it’s essential to seek medical attention for deep or gaping wounds, wounds caused by dirty or rusty objects, or if signs of infection develop.

Now that we’ve covered first aid for cuts and wounds, let’s move on to first aid for choking and CPR.
First Aid for Choking and CPR
Choking can be a life-threatening emergency, and immediate action is required to dislodge the object obstructing the airway. CPR, on the other hand, is a life-saving technique used when someone’s breathing or heartbeat has stopped. Here’s how you can provide first aid for choking and perform CPR:
- Determine if the person can speak or cough. If the person is coughing forcefully, encourage them to continue coughing to try and dislodge the object. If the person is unable to speak or cough, immediate action is required.
- Perform the Heimlich maneuver. Stand behind the choking person and place your arms around their waist. Make a fist with one hand and place it slightly above their navel. Grasp your fist with your other hand and give quick upward thrusts. Repeat until the object is expelled or the person can breathe again.
- Perform CPR if the person becomes unconscious. If the person becomes unconscious and is not breathing, it’s important to start CPR immediately. Follow these steps: a. Call for help and ask someone to bring an AED (Automated External Defibrillator), if available. b. Position the person on their back on a firm surface. c. Open the airway by tilting the head back and lifting the chin. d. Check for breathing and pulse. If absent or irregular, start CPR. e. Perform chest compressions by placing the heel of one hand on the center of the person’s chest and interlocking your fingers.