Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) has been a hot topic in healthcare for several years now. As women go through menopause, they experience a decline in hormone production, leading to a range of uncomfortable symptoms. HRT aims to alleviate these symptoms by replacing the hormones that the body is no longer producing in sufficient quantities.
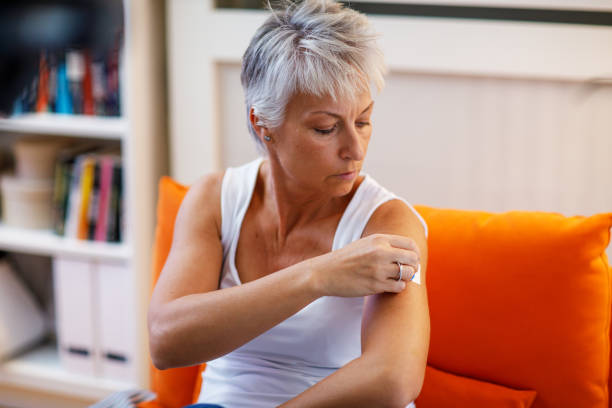

With debates surrounding the safety and efficacy of HRT, it’s essential to have accurate information at your fingertips. In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of Hormone Replacement Therapy, delving into its benefits, risks, and latest research findings. Whether you’re considering HRT or simply curious about its impact on women’s health, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of this treatment option.
What is Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)?
Hormone Replacement Therapy, or HRT, is a medical treatment that involves replacing the hormones that the body no longer produces in sufficient quantities. It is most commonly used to alleviate the symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood swings.
There are two main types of hormones that are typically replaced in HRT: estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen helps regulate the menstrual cycle and is responsible for the development and maintenance of female sexual characteristics. Progesterone is involved in the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy and helps regulate the menstrual cycle.
HRT can be prescribed in various forms, including pills, patches, gels, creams, and injections. The type and dosage of hormones prescribed will depend on factors such as age, symptoms, and overall health.
Common Reasons for Hormone Replacement Therap
HRT is primarily used to alleviate the symptoms of menopause, but there are other conditions and situations where it may be prescribed. Some common reasons for undergoing HRT include:
Menopause: The most common reason for HRT is to relieve the symptoms associated with menopause. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and can have a significant impact on a woman’s quality of life.
Surgical Menopause: If a woman undergoes surgical removal of her ovaries (oophorectomy) before natural menopause, she will experience an abrupt decline in hormone levels. HRT can help alleviate the symptoms of surgical menopause.
Premature Menopause: Some women experience menopause before the age of 40, which is known as premature menopause. HRT can provide relief from the symptoms and help reduce the risk of long-term health problems associated with early menopause.
Osteoporosis: Estrogen plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density. HRT can help prevent or slow down the progression of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and fragile bones.
Hormone Imbalance: In some cases, women may have a hormone imbalance that can be treated with HRT. This can occur due to conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or certain types of cancer treatment.
Benefits of Hormone Replacement Therapy
HRT offers several benefits for women experiencing menopause or other hormone-related conditions. Some of the potential benefits include:
Relief from Menopausal Symptoms: HRT can effectively alleviate the symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood swings. This can greatly improve a woman’s quality of life and overall well-being.
Improved Bone Health: Estrogen plays a vital role in maintaining bone density. HRT can help prevent or slow down the progression of osteoporosis, reducing the risk of fractures and other complications associated with weak bones.
Protection Against Heart Disease: Estrogen has a protective effect on the cardiovascular system, helping to reduce the risk of heart disease in premenopausal women. HRT may offer similar benefits in postmenopausal women, although the research in this area is still ongoing.
Enhanced Cognitive Function: Some studies suggest that estrogen may have a positive impact on cognitive function, particularly memory and verbal fluency. HRT may help improve cognitive function in postmenopausal women, although more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between hormones and brain health.
Relief from Vaginal Symptoms: HRT can alleviate vaginal dryness and discomfort, making sexual intercourse more comfortable and enjoyable for women experiencing menopause.
Risks and Side Effects of Hormone Replacement Therapy
While HRT offers several benefits, it is essential to understand the potential risks and side effects associated with this treatment option. The decision to undergo HRT should be made after a thorough discussion with a healthcare provider, weighing the potential benefits against the risks.
Increased Risk of Breast Cancer: One of the most significant concerns surrounding HRT is its potential link to an increased risk of breast cancer. Research has shown that long-term use of combination HRT (estrogen and progestin) may slightly increase the risk of breast cancer. However, the absolute risk remains relatively low, and the decision to use HRT should be based on individual circumstances and preferences.
Increased Risk of Blood Clots: HRT, particularly when taken orally, may increase the risk of blood clots. This risk is higher in women who have existing risk factors for blood clots, such as a history of clotting disorders or smoking.
Increased Risk of Stroke: Some studies have suggested that HRT, particularly combination therapy, may slightly increase the risk of stroke. The risk is highest in older women and those with other risk factors for stroke, such as high blood pressure or smoking.
Gallbladder Disease: The use of estrogen, particularly in higher doses, has been associated with an increased risk of gallbladder disease. This risk is more significant in women who already have gallbladder problems or a history of gallstones.
Other Side Effects: HRT can also cause other side effects, such as bloating, breast tenderness, headaches, and mood changes. These side effects are usually temporary and often improve with time or a change in medication.
Types of Hormone Replacement Therapy
There are different types of HRT available, including estrogen-only and combination therapy. The choice of HRT will depend on factors such as symptoms, medical history, and personal preferences.
Estrogen-Only Therapy: Estrogen-only therapy is typically prescribed for women who have had a hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus). Since there is no risk of uterine cancer in these women, they can safely take estrogen alone. Estrogen can be administered in the form of pills, patches, creams, gels, or vaginal rings.
Combination Therapy: Combination therapy involves the use of both estrogen and progestin. Progestin is added to protect the lining of the uterus and reduce the risk of uterine cancer. Combination therapy is typically prescribed for women who have not had a hysterectomy. It can be administered in various forms, including pills, patches, creams, gels, or intrauterine devices (IUDs).
Localized Therapy: Localized HRT involves the use of low-dose estrogen in the form of creams, rings, or tablets that are applied directly to the vagina. This type of therapy is primarily used for the treatment of vaginal symptoms, such as dryness and irritation.
The choice of HRT will depend on individual needs and preferences, as well as discussions with a healthcare provider.
Choosing a Hormone Replacement Therapy Provider
When considering HRT, it is essential to choose a healthcare provider who is knowledgeable and experienced in this area. Here are a few factors to consider when selecting a hormone replacement therapy provider:
Expertise and Experience: Look for a healthcare provider who specializes in menopause management and has experience in prescribing HRT. They should be up-to-date with the latest research and guidelines in this field.
Personalized Approach: Each woman’s needs and preferences are unique. A good provider will take the time to understand your specific symptoms, medical history, and goals. They will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that is tailored to your individual needs.
Communication and Trust: Building a good rapport with your healthcare provider is crucial. They should be approachable, willing to answer your questions, and provide you with clear and accurate information about HRT. Trust is essential in the doctor-patient relationship, especially when making decisions about your health.
Comprehensive Care: Look for a provider who offers comprehensive care, including regular follow-up visits and monitoring. They should be available to address any concerns or side effects that may arise during the course of your treatment.
The Process of Hormone Replacement Therapy
The process of undergoing HRT typically involves several steps, including:
Consultation: The first step is to schedule a consultation with a healthcare provider who specializes in menopause management. During this visit, your provider will take a detailed medical history, conduct a physical examination, and discuss your symptoms and treatment goals.
Hormone Evaluation: Based on your symptoms and medical history, your provider may order hormone level testing to evaluate your hormone levels. This can help determine the appropriate type and dosage of hormones for your treatment.
Treatment Plan: Once the evaluation is complete, your provider will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan. This may involve the prescription of HRT, as well as lifestyle modifications and other supportive therapies.
Monitoring: Regular follow-up visits will be scheduled to monitor your response to treatment and adjust the dosage if needed. Your provider may order additional tests to assess the effectiveness and safety of your HRT.
It’s important to communicate openly with your healthcare provider throughout the process, reporting any changes in symptoms or side effects. This will help ensure that your treatment is tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hormone Replacement Therapy
Is HRT safe for everyone?
HRT is generally safe for most women, but it may not be suitable for everyone. Factors such as medical history, personal preferences, and individual risk factors should be taken into consideration. It’s important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of HRT with a healthcare provider.
How long should I take HRT?
The duration of HRT will depend on individual circumstances. In most cases, HRT is prescribed for a short period, usually a few years, to alleviate menopausal symptoms. Long-term use may be considered for women with specific medical conditions, such as osteoporosis, or in cases where the benefits outweigh the risks.
Can I stop HRT cold turkey?
It is generally not recommended to stop HRT abruptly without consulting a healthcare provider. A gradual reduction in dosage is usually recommended to minimize the risk of withdrawal symptoms and to allow the body to adjust to the changes.
Are there alternative treatments to HRT?
Yes, there are alternative treatments to HRT that may help alleviate menopausal symptoms. These include lifestyle modifications, herbal remedies, and non-hormonal medications. It’s important to discuss these options with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment for your specific needs.
Can HRT increase my risk of breast cancer?
The use of HRT, particularly combination therapy, may slightly increase the risk of breast cancer. However, the absolute risk remains relatively low. It’s important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of HRT with a healthcare provider to make an informed decision.
Alternative Treatments to Hormone Replacement Therapy
While HRT is an effective treatment option for many women, it may not be suitable for everyone. Fortunately, there are alternative treatments available that can help alleviate menopausal symptoms. These include:

Lifestyle Modifications: Simple lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on menopausal symptoms. These include regular exercise, a healthy diet, stress reduction techniques, and getting enough sleep.
Herbal Remedies: Certain herbal remedies, such as black cohosh, soy, and red clover, have been used for centuries to alleviate menopausal symptoms. However, it’s important to discuss these remedies with a healthcare provider before use, as they may interact with other medications or have potential side effects.
Non-Hormonal Medications: There are several non-hormonal medications available that can help manage specific menopausal symptoms. These include antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs). These medications work by targeting specific symptoms, such as hot flashes or mood swings.
Complementary Therapies: Complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, yoga, and mindfulness meditation, have been found to be helpful in managing menopausal symptoms. These therapies focus on holistic well-being and can provide relief from symptoms.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any alternative treatments to ensure their safety and effectiveness for your specific needs.
Conclusion
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is a medical treatment that aims to alleviate the symptoms of menopause and other hormone-related conditions. It involves replacing the hormones that the body no longer produces in sufficient quantities. While HRT offers several benefits, it’s important to consider the potential risks and side effects associated with this treatment option.
By understanding the types of HRT available, the benefits and risks, and alternative treatment options, women can make informed decisions about their health and well-being. It’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider who specializes in menopause management to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and goals.
Remember, no two women are the same, and the decision to undergo HRT should be based on a thorough evaluation of individual circumstances. With accurate information and guidance, women can navigate the world of Hormone Replacement Therapy and make choices that promote their overall health and well-being.