scoliosis
Scoliosis is a common spinal condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine, scoliosis can cause pain, discomfort, and even affect one’s overall quality of life. From adolescents to adults, this condition can strike at any age, making it important to understand its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
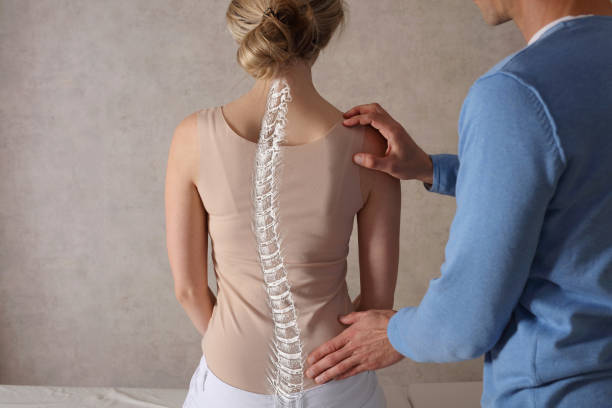
In this comprehensive guide to scoliosis, we will delve into the intricacies of this condition, shedding light on its various forms, such as idiopathic scoliosis, congenital scoliosis, and degenerative scoliosis. We will explore the common signs and symptoms to watch out for, including uneven shoulders, an asymmetrical waistline, and a noticeable curve in the spine.
What is scoliosis?
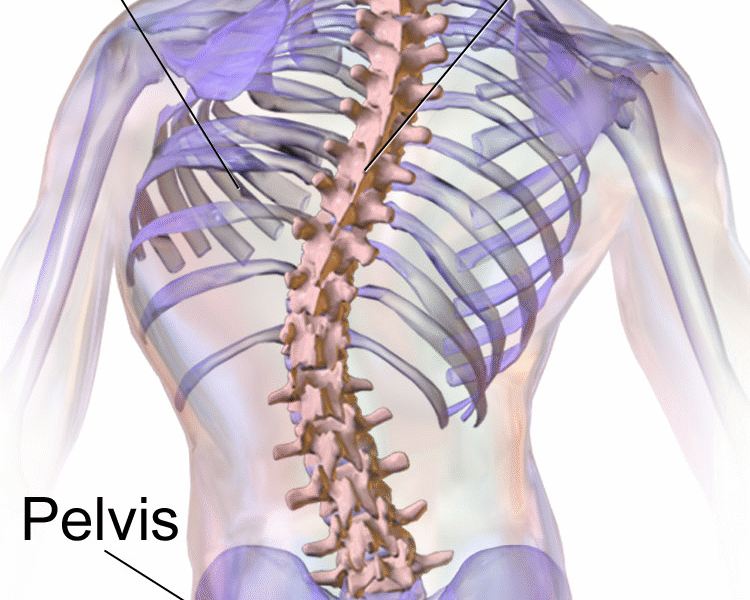
Scoliosis is a spinal condition that is characterized by an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine. Instead of the spine being straight, it curves to the left or right, resembling the letter “S” or “C.” This curvature can vary in severity, and in some cases, it can even cause the spine to rotate, leading to additional complications. Scoliosis can occur at any age, but it is most commonly diagnosed during adolescence when rapid growth occurs.
There are several different types of scoliosis, including idiopathic scoliosis, which is the most common form and has no known cause. Congenital scoliosis is present at birth and is caused by abnormal spinal development in the womb. Degenerative scoliosis occurs later in life and is typically a result of the wear and tear on the spine due to aging.
Causes and risk factors of scoliosis
The exact cause of idiopathic scoliosis, the most prevalent form of scoliosis, remains unknown. However, research suggests that it may be influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some studies have identified certain genes that may predispose individuals to develop scoliosis, while others suggest that hormonal imbalances during puberty could play a role.
In addition to genetics and hormones, other risk factors for developing scoliosis include a family history of the condition, certain neuromuscular conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy, and certain connective tissue disorders. It’s important to note that while these risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing scoliosis, they do not guarantee its occurrence.
Symptoms and signs of scoliosis
The signs and symptoms of scoliosis can vary depending on the severity of the curvature and the age of the individual. In some cases, scoliosis may cause no noticeable symptoms, while in others, it can lead to pain, discomfort, and visible physical changes. Common signs to watch out for include:
- Uneven shoulders: One shoulder may appear higher or more prominent than the other.
- Asymmetrical waistline: The waistline may appear uneven, with one side higher or more pronounced than the other.
- Noticeable curve in the spine: A visible curvature of the spine may be present, especially when bending forward.
It’s important to note that these signs and symptoms may not be immediately obvious, especially in mild cases of scoliosis. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are essential for early detection and diagnosis.
Diagnosing scoliosis
Diagnosing scoliosis typically involves a physical examination and, if necessary, additional imaging tests. During the physical examination, a healthcare professional will assess the individual’s posture, range of motion, and physical appearance. They may also measure the curvature of the spine using a scoliometer or conduct a scoliosis screening test.
If scoliosis is suspected, further imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, may be ordered to assess the severity and location of the curvature. These tests can provide detailed images of the spine, allowing healthcare professionals to determine the best course of treatment.
Treatment options for scoliosis
The treatment options for scoliosis vary depending on the severity of the curvature, the age of the individual, and other factors. In mild cases, regular monitoring and conservative approaches may be sufficient, while more severe cases may require surgical intervention. The goal of treatment is to prevent further progression of the curve, alleviate pain and discomfort, and improve overall function and quality of life.
Non-surgical approaches for scoliosis
Non-surgical approaches for scoliosis focus on managing the condition through a combination of conservative therapies. These may include:
- Physical therapy: Targeted exercises and stretches can help strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve posture.
- Bracing: In some cases, a brace may be recommended to help halt the progression of the curvature, particularly during periods of rapid growth.
- Pain management techniques: Pain medication, heat or cold therapy, and other pain management strategies can help alleviate discomfort associated with scoliosis.
It’s important to note that non-surgical approaches are typically more effective in adolescents whose bones are still growing and more responsive to treatment.
Surgical interventions for scoliosis
In severe cases of scoliosis or when conservative approaches have failed to effectively manage the curvature, surgical intervention may be recommended. The specific surgical procedure will depend on the individual’s age, the severity of the curvature, and other factors. Common surgical interventions for scoliosis include:
- Spinal fusion: This procedure involves fusing together two or more vertebrae to create a solid bone, which helps straighten and stabilize the spine.
- Rod insertion: Metal rods may be inserted along the length of the spine to correct the curvature and provide additional support.
- Vertebral body tethering: This newer surgical technique involves attaching a flexible cord to the spine to correct the curvature while allowing for continued growth.
Surgical interventions for scoliosis are typically considered a last resort and are only recommended when the benefits outweigh the risks.
Living with scoliosis: Coping strategies and support
Living with scoliosis can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It’s important for individuals with scoliosis to develop coping strategies and seek support when needed. Here are some tips for living with scoliosis:
- Maintain good posture: Practicing good posture can help alleviate pain and prevent further progression of the curvature.
- Stay active: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as swimming or yoga, can help strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve overall flexibility.
- Seek support: Connecting with others who have scoliosis, joining support groups, or seeking counseling can provide emotional support and guidance.
Remember, scoliosis does not define you, and with the right support and self-care, individuals with scoliosis can lead fulfilling lives.
Preventing scoliosis
While it may not be possible to prevent scoliosis entirely, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk or detect it early
- Regular check-ups: Routine check-ups with a healthcare professional can help identify any signs or symptoms of scoliosis early on.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight can contribute to overall spine health.
- Being aware of risk factors: Understanding the risk factors associated with scoliosis, such as family history or certain medical conditions, can help individuals take proactive measures.
By staying informed and taking proactive steps, individuals can potentially reduce the impact of scoliosis on their lives.
Conclusion
Scoliosis is a complex spinal condition that can significantly impact an individual’s life. Understanding the different forms of scoliosis, its causes, and the available treatment options is essential for individuals living with this condition. Whether it’s through non-surgical approaches like physical therapy and bracing or surgical interventions in severe cases, there are options available to manage scoliosis and improve quality of life. With the right support and self-care, individuals with scoliosis can lead fulfilling lives, embracing their uniqueness and navigating the challenges with resilience and strength.