What Is Formal Education And The Four Stages Of Formal Education
Formal education is the foundation of knowledge and skills that shape individuals into well-rounded and knowledgeable members of society. In this article, we will explore what formal education is and delve into the four stages of formal education.
The Importance of Formal Education
Formal education refers to the structured educational system provided by schools, colleges, and universities. It follows a specific curriculum and is typically led by trained and qualified educators. This type of education is essential as it provides individuals with a solid educational foundation and equips them with the necessary skills to pursue their chosen career paths.

Education is the key to personal and professional growth. It opens doors to opportunities, enhances critical thinking skills, and fosters intellectual development. Formal education plays a crucial role in shaping individuals’ knowledge, values, and attitudes, preparing them to become active and responsible members of society.
The Four Stages of Formal Education
The four stages of formal education are commonly known as primary, secondary, higher, and tertiary education. Each stage serves a specific purpose in an individual’s educational journey, from laying the groundwork for learning in primary education to focusing on specific subject areas in secondary education, to the specialized knowledge gained in higher and tertiary education.
Early Childhood Education
Early childhood education, also known as preschool or kindergarten, is the first stage of formal education. This stage typically caters to children aged three to six years old and focuses on developing their social, emotional, cognitive, and physical skills. Early childhood education provides a nurturing and stimulating environment for young learners, laying the foundation for their future academic success.
During this stage, children engage in play-based learning activities that promote their overall development. They learn to interact with their peers, follow instructions, and develop early literacy and numeracy skills. Early childhood education aims to foster a love for learning and prepare children for the next stage of formal education.
Primary Education
Primary education, also known as elementary school, is the second stage of formal education. It usually begins around the age of six or seven and lasts for several years, depending on the country’s educational system. Primary education focuses on providing students with a broad range of knowledge and skills across various subject areas.
At this stage, students acquire foundational skills in literacy, numeracy, science, social studies, and physical education. They develop critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and the ability to work collaboratively. Primary education aims to build a strong educational foundation and instill a love for learning in students.
Secondary Education
Secondary education, also known as high school, is the third stage of formal education. It typically begins around the age of twelve or thirteen and lasts for several years. Secondary education builds upon the knowledge and skills acquired in primary education and offers more specialized subject areas.
At this stage, students have the opportunity to choose elective subjects based on their interests and career aspirations. They delve deeper into subject areas such as mathematics, sciences, humanities, languages, and the arts. Secondary education aims to prepare students for higher education or vocational training and equips them with the skills necessary for future employment.
Tertiary Education
Tertiary education, also known as higher education, is the final stage of formal education. It usually takes place at colleges, universities, or vocational institutions after completing secondary education. Tertiary education offers specialized knowledge and skills in specific subject areas, preparing students for their chosen careers.
At this stage, students have the opportunity to pursue undergraduate and postgraduate degrees, diplomas, or certifications. Tertiary education provides advanced learning opportunities, research opportunities, and practical experiences in various fields. It equips individuals with the knowledge, skills, and competencies necessary for their professional lives.
Characteristics and Goals of Each Stage
Each stage of formal education has its own unique characteristics and goals. Early childhood education focuses on developing foundational skills and preparing children for primary education. Primary education aims to provide a broad range of knowledge and skills across various subject areas. Secondary education offers more specialized subject areas and prepares students for higher education or vocational training. Tertiary education provides specialized knowledge and skills for specific careers.
The goals of formal education include fostering intellectual development, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills, developing effective communication and collaboration skills, and preparing individuals for future employment or further education. Each stage contributes to the overall growth and development of individuals, preparing them for success in various aspects of life.
Pros and Cons of Formal Education
While formal education offers numerous benefits, it also has its own share of pros and cons.
Some of the pros include:
- Access to structured learning: Formal education provides a structured learning environment with a defined curriculum, which ensures that individuals acquire a comprehensive set of knowledge and skills.
- Qualified educators: Formal education is led by trained and qualified educators who provide guidance, support, and expertise.
- Recognition and credentials: Formal education provides individuals with recognized qualifications and credentials, which can enhance their employability and career prospects.
However, there are also some cons:
- Limited flexibility: Formal education follows a set curriculum, which may limit individual creativity and flexibility in learning.
- Standardized assessments: Formal education often relies on standardized assessments, which may not accurately measure an individual’s true abilities or potential.
- Cost: Formal education can be expensive, especially at the higher and tertiary levels, making it inaccessible for some individuals.
The Role of Formal Education in Society
Formal education plays a crucial role in society. It equips individuals with the necessary knowledge, skills, and competencies to contribute to the growth and development of their communities. Formal education promotes social mobility, equal opportunities, and social cohesion.
In addition to providing individuals with the knowledge and skills they need for their chosen careers, formal education also fosters personal growth, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities. It encourages individuals to become active and responsible citizens, promoting democratic values, social justice, and ethical behavior.
Challenges and Criticisms of Formal Education
Despite its importance, formal education faces various challenges and criticisms. Some common challenges include

- Inadequate resources: Many educational institutions face resource constraints, such as lack of funding, outdated infrastructure, and limited access to technology.
- Inequality in access: Access to quality formal education is not equitable worldwide. Many individuals, especially those from disadvantaged backgrounds or rural areas, face barriers in accessing educational opportunities.
- Standardized approach: The standardized approach of formal education may not cater to the diverse learning needs and preferences of individuals.
Critics argue that formal education focuses too much on academic achievement and standardized assessments, neglecting the development of practical skills, creativity, and emotional intelligence. They advocate for more student-centered and holistic approaches to education.
The Future of Formal Education
The future of formal education is evolving rapidly due to advancements in technology, changing societal needs, and global challenges. The digital age has revolutionized the way education is delivered, with online learning platforms, virtual classrooms, and personalized learning experiences becoming increasingly prevalent.
In the future, formal education is likely to become more flexible, individualized, and accessible. Blended learning models, combining online and face-to-face instruction, will become more common. Technology will continue to play a significant role in enhancing teaching and learning experiences.
Moreover, there will be a greater emphasis on developing 21st-century skills such as critical thinking, creativity, adaptability, and digital literacy. Formal education will also need to address global challenges, such as sustainability, social justice, and cultural diversity.
Alternative Education Options
While formal education is widely recognized and valued, alternative education options have gained popularity in recent years. Alternative education options offer different approaches to learning and cater to specific needs and preferences.
Some alternative education options include:
- Homeschooling: Parents or guardians take on the responsibility of educating their children at home, following a personalized curriculum.
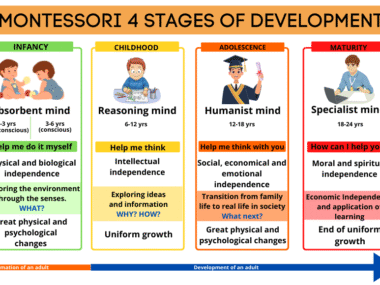
- Montessori education: Based on the principles developed by Maria Montessori, this approach focuses on individualized learning, hands-on experiences, and self-directed discovery.
- Waldorf education: Inspired by the philosophy of Rudolf Steiner, Waldorf education emphasizes holistic development, artistic expression, and experiential learning.
- Vocational training: Vocational training programs provide individuals with specific skills and knowledge required for a particular trade or industry.
Alternative education options offer flexibility, personalized learning experiences, and a focus on individual strengths and interests. They provide alternatives to the traditional formal education system and cater to diverse learning needs.
Conclusion
Formal education is a vital foundation for personal and professional growth. By understanding the concept of formal education and its various stages, individuals can make informed decisions about their educational journey and pave the way for lifelong learning and success.
The four stages of formal education, from early childhood education to tertiary education, provide individuals with a comprehensive set of knowledge, skills, and competencies. Each stage contributes to personal and intellectual development, preparing individuals for future endeavors.
While formal education has its pros and cons, it plays a significant role in society by promoting social mobility, equal opportunities, and personal growth. It equips individuals with the necessary tools to contribute to their communities and make a positive impact on the world.
As formal education continues to evolve, it is essential to address the challenges it faces and explore alternative education options that cater to diverse learning needs. The future of formal education will be shaped by advancements in technology, changing societal needs, and a greater focus on holistic and individualized approaches to learning.
Unlocking the power of formal education is the key to unlocking a world of opportunities and possibilities. Embrace the transformative journey of formal education and embark on a lifelong quest for knowledge, growth, and success.