What Is Irritable Bowel Syndrome
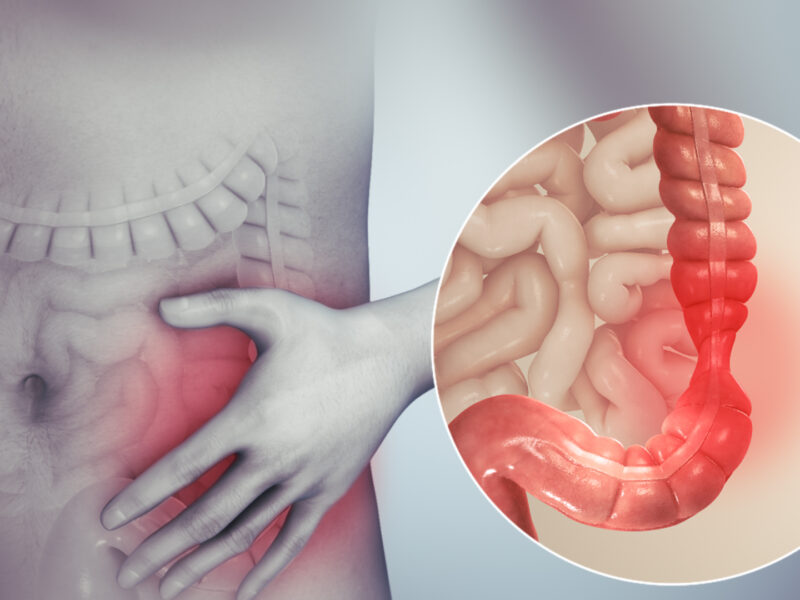
If you’ve ever experienced abdominal pain, bloating, or irregular bowel movements, you may be familiar with the frustrating and often debilitating condition known as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Affecting millions of people worldwide, IBS is a chronic disorder that affects the large intestine and can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Understanding the symptoms of IBS
The symptoms of IBS can vary from person to person, making it a tricky condition to diagnose. Common signs include abdominal pain or cramping, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation. These symptoms can be mild or severe and may come and go over time.
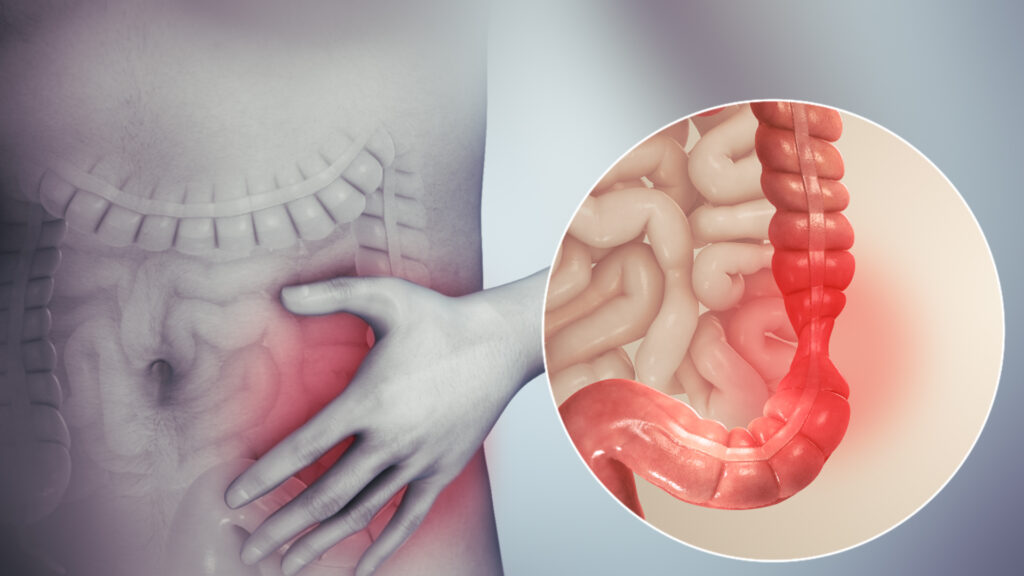
One of the key aspects of understanding IBS is recognizing the various symptoms that individuals may experience. Abdominal pain or cramping is a common complaint among those with IBS, and it can range from mild discomfort to severe pain. Bloating and gas are also prevalent symptoms, often causing discomfort and a feeling of fullness. Additionally, individuals with IBS may experience irregular bowel movements, including diarrhea and constipation, which can further disrupt their daily lives.
It’s important to note that while these symptoms are characteristic of IBS, they can also be indicative of other gastrointestinal conditions. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Causes and triggers of IBS
While the exact cause of IBS remains unknown, researchers believe that various factors contribute to its development. One such factor is abnormal intestinal contractions, which can cause the muscles in the intestines to contract either too forcefully or too weakly. This irregularity can lead to changes in bowel movements and contribute to the symptoms experienced by individuals with IBS.
Another potential factor is the presence of changes in gut bacteria. The gut is home to trillions of bacteria, collectively known as the gut microbiota, which play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. Disruptions in the balance of these bacteria can potentially contribute to the development of IBS.
Additionally, individuals with IBS often exhibit increased sensitivity to pain, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract. This heightened sensitivity can lead to exaggerated pain responses to normal stimuli, further exacerbating the symptoms of IBS.
It’s important to note that while these factors may contribute to the development of IBS, they do not necessarily cause the condition in every individual. The exact interplay between these factors and the gut-brain interaction in IBS is still being studied.
Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Diagnosing IBS can be challenging due to the wide range of symptoms and the absence of definitive tests. Healthcare professionals typically rely on a combination of medical history, physical examination, and the presence of specific criteria to make a diagnosis.
To diagnose IBS, healthcare professionals will first evaluate the individual’s medical history, paying close attention to their symptoms, their duration, and any factors that may exacerbate or alleviate their symptoms. They will also perform a physical examination to rule out other potential causes of the symptoms.
In some cases, additional tests may be ordered to rule out other conditions. These tests may include blood tests, stool tests, imaging tests, or endoscopic procedures. While these tests are not diagnostic for IBS, they can help identify other potential causes of the symptoms.
Once other conditions have been ruled out and the criteria for IBS are met, a diagnosis can be made. It’s important to note that the diagnosis of IBS is typically based on the presence of specific symptoms and the absence of any red flags or warning signs that may indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Common misconceptions about IBS
There are several common misconceptions about IBS that can lead to misunderstandings and frustration for individuals living with the condition. One common misconception is that IBS is all in the individual’s head or purely psychological. While stress and emotions can certainly exacerbate symptoms, IBS is a physical disorder that affects the gut-brain interaction.
Another misconception is that IBS is a rare condition. In reality, IBS is quite common, affecting millions of people worldwide. However, due to the nature of the condition and the stigma surrounding digestive disorders, many individuals may suffer in silence and go undiagnosed.
It’s also important to dispel the notion that IBS is a minor inconvenience or simply a “nervous stomach.” For many individuals, IBS can significantly impact their quality of life, causing pain, discomfort, and disruptions in daily activities.
Managing IBS through lifestyle changes
While there is no known cure for IBS, there are various strategies and lifestyle changes that can help manage and alleviate symptoms. One of the first steps in managing IBS is identifying and avoiding triggers. Triggers can vary from person to person but may include certain foods, stress, hormonal changes, and even environmental factors.
Keeping a food diary can be helpful in identifying trigger foods. By noting what you eat and any symptoms that arise, you can begin to identify patterns and make informed decisions about your diet. It’s important to note that trigger foods can vary greatly among individuals, so what works for one person may not work for another.
In addition to dietary changes, stress management techniques can also be beneficial in managing IBS symptoms. Stress can exacerbate symptoms and contribute to gut dysfunction, so finding healthy coping mechanisms such as exercise, meditation, or therapy can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.
Medications and treatments for IBS
In some cases, healthcare professionals may recommend medications to help manage IBS symptoms. These medications can include antispasmodics, which help reduce abdominal pain and cramping, and anti-diarrheal agents, which can help control diarrhea.
For individuals with constipation-predominant IBS, laxatives or medications that promote bowel movements may be prescribed. Additionally, certain antidepressant medications can be beneficial in managing IBS symptoms by targeting the gut-brain interaction.
It’s important to note that medications should always be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional, as they can have side effects and interactions with other medications.
Alternative therapies for IBS
In addition to conventional treatments, some individuals find relief from IBS symptoms through alternative therapies. These therapies can include acupuncture, herbal supplements, probiotics, and mind-body techniques such as hypnotherapy.
While the effectiveness of these therapies may vary among individuals, some studies have shown promising results. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative therapies to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your specific situation.
Diet and nutrition tips for individuals with IBS
Diet plays a crucial role in managing IBS symptoms. While trigger foods can vary among individuals, some common culprits include fatty foods, spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, and certain types of carbohydrates, such as those found in wheat, onions, and legumes.
One approach that has shown promise in managing IBS symptoms is the low FODMAP diet. FODMAPs are a group of carbohydrates that are poorly absorbed in the small intestine and can ferment in the colon, leading to symptoms such as bloating and gas. By temporarily eliminating high FODMAP foods and gradually reintroducing them, individuals can identify which specific foods trigger their symptoms.
It’s important to note that the low FODMAP diet should be undertaken with the guidance of a registered dietitian or healthcare professional to ensure proper nutrition and prevent any potential nutrient deficiencies.
Conclusion and final thoughts
In conclusion, Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a chronic disorder that affects the large intestine and can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. While the exact cause of IBS is still unknown, researchers believe that a combination of factors, including abnormal intestinal contractions, changes in gut bacteria, and increased sensitivity to pain, play a role in its development.
Managing IBS involves understanding the symptoms, identifying triggers, and making necessary lifestyle changes. Medications and alternative therapies may also be used to alleviate symptoms. Additionally, diet and nutrition play a crucial role in managing IBS, and individuals may find relief by following a low FODMAP diet or identifying trigger foods through a food diary.
If you suspect you may have IBS, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to receive an accurate diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan. While there is no known cure for IBS, with the right management strategies, individuals can take control of their symptoms and improve their quality of life.